Talisman. Social media analysis technology
The term "social media" commonly refers to online social networks, forums, blogs, news sites and other services that allow its users to interact with each other by exchanging messages, commenting, rating, etc. Social media are unique sources of data on personal life, opinions and interests of real people. Analysis of social media allows more effective solving problems of marketing, recommending goods and services, information extraction and many others.
Social data processing requires algorithmic and infrastructural solutions that allow us to account for large data size, informal language of communication, the possibility to hide author's personality, and other data specifics. For example, the Facebook database contains more than 1 billion user accounts and more than 100 billion links between them. Every day, users add more than 200 million photos and leave more than 2 billion comments on various objects of the network.
ISP RAS has developed a number of original methods for social analysis which were combined into a technology called TALISMAN. Unlike most existing solutions for social analytics, TALISMAN technology was originally aimed at working with large amounts of data. The most promising open solutions from the stack of Big Data technologies are employed, such as: Apache Spark, GraphX, MLLib, etc.
Data collection from social media
The first problem faced by the developers of social media analysis tools is obtaining complete and up-to-date information. The data collection tool from TALISMAN stack helps collect data from social networks (VKontakte, Facebook, Twitter), blogs (LiveJournal) and news sites (ria.ru, lenta.ru, etc). Different ways to sample user accounts from social media sites are supported. Automatic selection of social network account for each request is implemented, as well as support for proxy connections. In addition, multi-threaded downloading is supported. At the same time, due to the rapid development of social media technologies, the tool makes it possible to quickly add new downloading scenarios, sampling methods and resources.
However, collecting real data is often costly, in terms of time and other resources.
Furthermore, statistical characteristics of the obtained social graphs are fixed without the possibility of changing. Another part of TALISMAN is a tool for generating random graphs exhibiting basic properties of social networks (degree distribution, diameter, clustering coefficient, user communities, etc.). The proposed method has a distributed implementation based on Apache Spark which can create random large-scale social graphs to test performance and quality of social data analysis methods.
Information flow monitoring
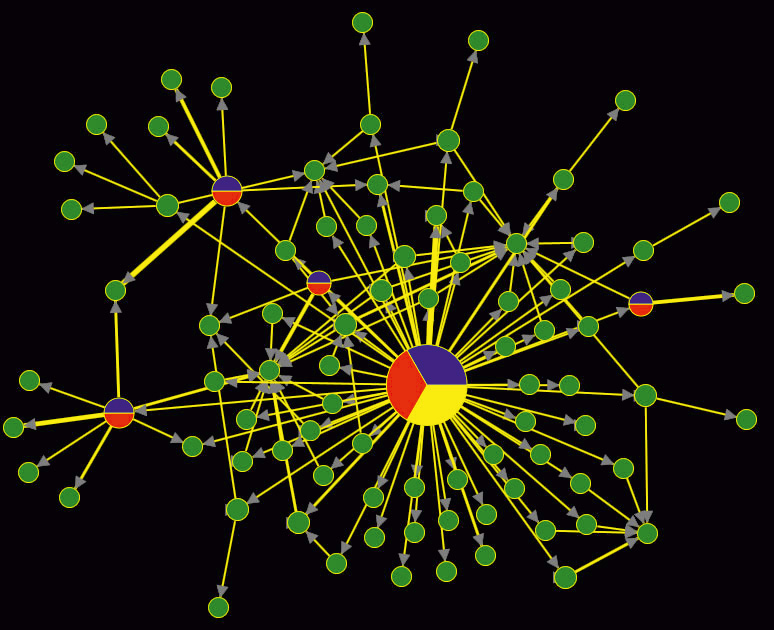
Monitoring of information flows assumes continuous following of social media streams and analysis of references to the objects of interest. TALISMAN identifies typical ways of information dissemination and determines the roles of users and individual resources in this process. Possible roles include original sources of information, distributors, readers and opinion leaders. The most important characteristics of monitoring systems are speed and completeness. TALISMAN allows building solutions that surpass analogs in both parameters. Using of systems for processing big data streams inside TALISMAN leads to high analysis speed: analytical reports on objects of interest are provided within a few minutes after publication of information.
Figure 1. Communicative interaction graph of Facebook users in the discussion of power outage in Crimea on November 30, 2015. The nodes are users, oriented links denote the direction of information dissemination. Color denotes user roles: yellow - original source, red – opinion leader, blue - distributor, green - reader.
Completeness of object search results is achieved using semantic analysis tool of the Texterra technology. It allows finding object references taking into account specific language of comments (internet slang, hashtags, accidental and intentional misspells). Also, Texterra analyzes user opinions on objects and their attributes (for example, it can understand if a person expresses a negative opinion on usability of a device, but at the same time recommends the screen).
TALISMAN also includes tools to filter out spam, report bots, and identify negative emotions in relation to other participants of discussion.
Restoring incomplete or incorrect user profiles In systems for Internet marketing and recommendations, it is of particular importance to determine socio-demographic user attributes for targeted promotion of goods and services among the target audience. However, users often by mistake or intentionally leave blank certain fields of their social network profile or give false information about facts of their biography, interests and preferences. In addition, the user profile is often limited to a set of basic attributes (name, gender) which is insufficient for many tasks connected with results personalization.
TALISMAN applies modern methods of machine learning to user attribute prediction, using social connections, messages and other available information about users (likes, reposts, subscriptions) as features. For a given account, it's possible to determine gender, age, marital status, educational level, religious/political views, and location, even if they were not explicitly provided by the user. In addition, TALISMAN does not rely on user-defined attribute values. It allows incorrect attribute values, as well as users whose behavior does not correspond to the information stated in his/her profile.
User community detection based on social link analysis
The natural property of human society is the tendency to form communities. A similar pattern is observed in social networks, where users are united either explicitly, by creating groups and interacting within them, or implicitly, by establishing connections based on similar interests, roles, social circles, etc.
Figure 2. User ego-network with detected communities (two main communities are highlighted in blue and green).
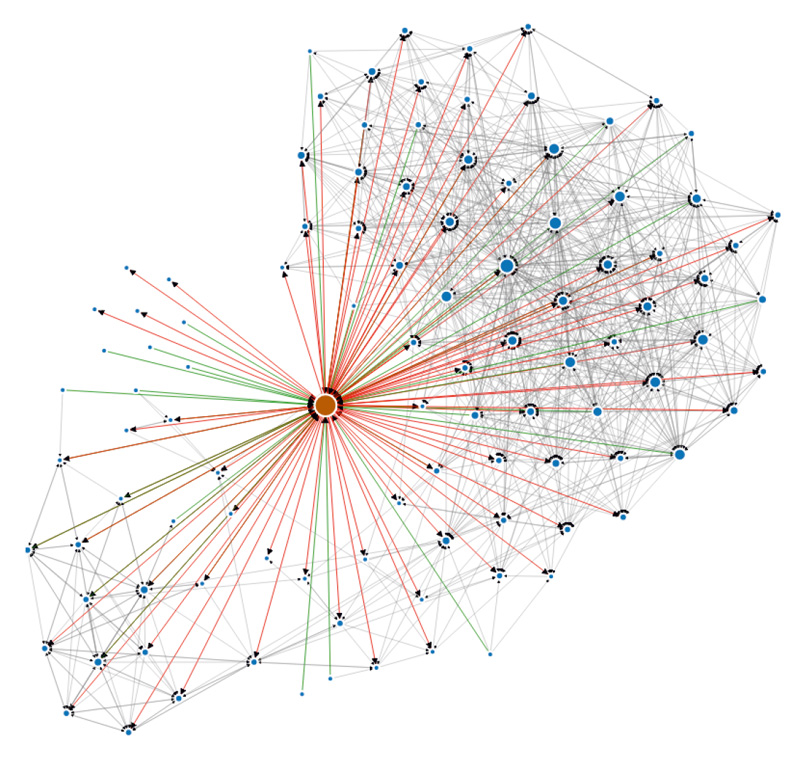
User community detection is an important tool for studying and analyzing social networks, that helps explore modular organization of the network. Community structure is being successfully used to predict connections and attributes of users, calculate proximity of users in social graph, optimize data flows in social network, develop recommendations systems, filter spam and other applications.
TALISMAN includes a set of methods for revealing implicit communities of social network users based on social connections between them. These methods can detect communities among user friends (ego-network) or in the entire social network.
User identity resolution
One of the fundamental problems when using social information about a user is its fragmentation among a number of social networks. For active Internet users it is typical to participate in several social networks. Detecting accounts belonging to the same person in different social networks leads to a more complete social graph. This can be useful in many tasks, such as information search, Internet advertising, recommender systems, etc.
A method has been developed for identifying users of various social networks, which boils down to searching for various identities of the same user in several social networks. The approach is based on probabilistic graphical model of conditional random field. The model accounts for similarity of user attributes and relationships with other users.
The developed user identity resolution method utilizes social connections of both input social networks by comparing contact lists and naturally combining them with profile information, thereby eliminating disadvantages of existing analogous methods.



